How Does a Gas Wall Furnace Work?
Published on : May 2nd, 2024

Gas wall furnaces offer a reliable and economical heating solution for many Australian homes. These units use natural gas to distribute warm air efficiently throughout the living space, making them a preferred choice for both small spaces and whole-house applications.
These heating systems, often referred to as wall gas heaters or wall-mounted heaters, are designed to be energy efficient and cost-effective.
Whether integrated into existing wall furnaces or installed as new units, they operate by burning natural gas to produce heat, which is then propelled into the room as heated air through a vent system. Safety features, such as carbon monoxide detectors, are crucial given the risks associated with combustion.
Understanding how gas wall furnace heaters work not only involves appreciating their functional mechanics − such as the gas valve, pilot light, and exhaust pipe − but also recognising their advantages in terms of running costs and energy consumption compared to electric wall heaters.
This introduction sets the stage for a deeper dive into the intricate workings of gas heating systems, their components and the benefits they bring to Australian homes.
What is a Wall Furnace?
A wall furnace, often referred to as a wall gas heater or wall mounted heater, is a heating system designed to provide targeted warmth to specific areas or rooms within a home. These units are particularly effective in climates where central heating may not be necessary or cost-effective, making them a popular choice in many Australian homes.
Wall furnaces can be vented or vent-free, with vented wall heaters expelling exhaust gases outside through a flue, thereby reducing the risk of indoor air pollutants like carbon monoxide. Unflued or vent-free heaters, on the other hand, do not require external venting, which makes them easier to install but necessitates adequate room ventilation to manage combustion by-products effectively.
The installation of a wall furnace typically involves a licensed professional who ensures that gas lines are correctly connected and that the unit is safely secured.
Post-installation, a final inspection by a city inspector may be required to ensure the system adheres to local safety regulations, emphasising the importance of professional installation and maintenance to optimise the furnace’s efficiency and safety.
Components of a Gas Wall Furnace
A gas wall furnace consists of several key components that work together to provide efficient and safe heating. Understanding these parts can help homeowners maintain their heating system effectively.
The heat exchanger is the core component where the heating process occurs. It absorbs the heat from the burning gas and transfers it to the air that circulates within the furnace. This part is crucial for the efficiency of the unit and needs regular checks to ensure it’s free from dust and corrosion.
Burners ignite the gas, starting the heating process. In systems like blue flame heaters and vented gas heaters, the burners must function correctly to maintain efficiency and safety. Regular cleaning, often with a vacuum cleaner or damp cloth, is necessary to prevent blockages and ensure optimal operation.
The blower or fan then pushes the heated air into the living space while drawing in cool air to be warmed. This circulation is essential for maintaining even temperatures throughout the room or home. Ensuring that this component is clear of debris will enhance the system’s overall efficiency.
Venting systems in vented wall heaters expel combustion gases to the outside, making them crucial for safety and preventing the build up of harmful pollutants. Unflued gas heaters, alternatively, require adequate room ventilation to maintain fresh air quality.
Lastly, the thermostat regulates the temperature by signalling the furnace to turn on or off based on the desired settings. Regular testing and calibration of the thermostat are important for energy efficiency and to avoid overuse of electricity, ensuring the space maintains a comfortable temperature consistently.
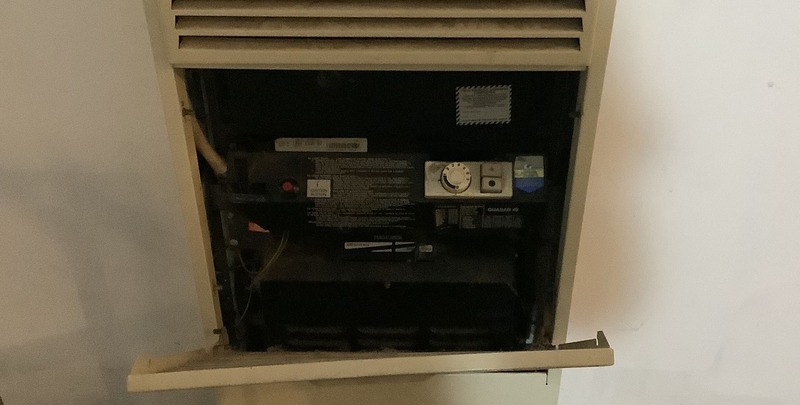
How a Gas Wall Furnace Works
Understanding the operational mechanics of a gas wall furnace provides homeowners insight into how efficiently and safely these appliances heat their space. The process is a systematic flow of events that begins when the thermostat detects a drop in temperature.
- Thermostat activation: The process starts with the thermostat, which monitors the room temperature. When the temperature falls below the set point, the thermostat signals the furnace to begin heating. This component is crucial for maintaining comfort and energy efficiency, ensuring the furnace operates only when necessary.
- Gas ignition: Upon receiving the signal from the thermostat, the gas valve opens, allowing natural gas to flow to the burners. In appliances such as blue flame heaters and vented gas heaters, an ignition system lights the gas, creating a controlled flame. This flame is the primary source of heat within the furnace.
- Heat exchange: The burning gas generates heat, which is captured by the heat exchanger. This component is essential in transferring heat from the flame to the air without allowing combustion gases to mix with the circulating air.
- Air circulation: A fan or blower activates to draw in cool air from the room, which passes over the hot heat exchanger. As the air warms up, it is pushed back into the room as warm air, effectively raising the room’s temperature.
- Venting combustion gases: In vented wall heater systems, combustion gases are expelled safely outside through a flue or vent, ensuring no harmful gases remain in the living space. This system is crucial for maintaining indoor air quality and preventing potential hazards.
- Cycle completion: Once the room reaches the desired temperature, the thermostat signals the furnace to shut off the burners, stopping the heating process. The blower may continue to run for a short period to utilise remaining heat from the heat exchanger.
Regular maintenance, such as removing dust from vents and ensuring the gas log fires are clean, is essential for the efficient and safe operation of the furnace. A gas utility professional can provide routine checks and maintenance to ensure the system operates at its best.
Advantages of Using a Gas Heater
Gas heaters, including ducted gas heaters and blue flame heaters, offer several advantages that make them a popular choice for heating homes efficiently and effectively.
- Energy efficiency: One of the most significant benefits of gas heaters is their energy efficiency. Gas appliances generally use less energy than electric heaters, making them an economical option for reducing heating costs. Vented heaters, in particular, can efficiently expel exhaust outside, preventing heat loss and maximising energy usage.
- Heating effectiveness: Gas heaters are capable of warming up a space quickly compared to electric heaters. Whether it’s a central system designed to heat an entire home or a single-room space heater, gas units provide rapid heat that is evenly distributed throughout the space.
- Cost-effectiveness: Over time, the initial installation and running costs of gas heaters can be lower than those of electric heaters, especially in areas where gas is comparatively cheaper than electricity. This makes them a cost-effective choice for long-term heating solutions.
- Design flexibility: Modern gas heaters come in various designs, including sleek radiator-style models and compact space heaters that can be easily integrated into any room without disrupting the decor. Regular maintenance like removing dust can keep these units running efficiently and safely for years, adding to their overall appeal as a practical heating solution.

Maintenance Tips for Your Wall Furnace
Proper maintenance is crucial for ensuring your gas wall furnace operates safely and efficiently. Here are some essential tips to keep your heating system in top condition.
- Regular cleaning: Dust can accumulate in and around your furnace, particularly in systems like ducted gas heaters and blue flame heaters. Regularly removing dust from the exterior and accessible components can prevent airflow blockages and maintain energy efficiency. Use a vacuum cleaner with a soft brush attachment to gently clean the unit.
- Annual inspections: Schedule an annual inspection with a qualified technician to check for any issues that might not be visible or obvious. This includes checking gas lines, burners, and connections for leaks or wear.
- Check and replace filters: If your system has filters, check them every few months and replace them as needed to ensure efficient airflow. This is especially important in one-room heaters, where air quality directly impacts living space comfort.
Adhering to these maintenance tips helps extend the life of your furnace and ensures it remains an energy-efficient option for heating your home.
Maximise Efficiency and Comfort
Understanding how a gas wall furnace works and its benefits can significantly impact your decision on home heating solutions. From the efficient heat distribution of a ducted gas heater to the cosy warmth of a blue flame heater, these systems offer reliable and cost-effective heating options.
Regular maintenance, including removing dust and periodic checks, ensures these heaters operate at peak efficiency and safety. Whether you’re upgrading your current system or considering a new installation, the right knowledge and care can help you make the most of your heating investment.
Please note: This information is provided for advice purposes only. Regulations differ from state to state, so please consult your local authorities or an industry professional before proceeding with any work. See our Terms & Conditions here.